japanese beetle life cycle iowa
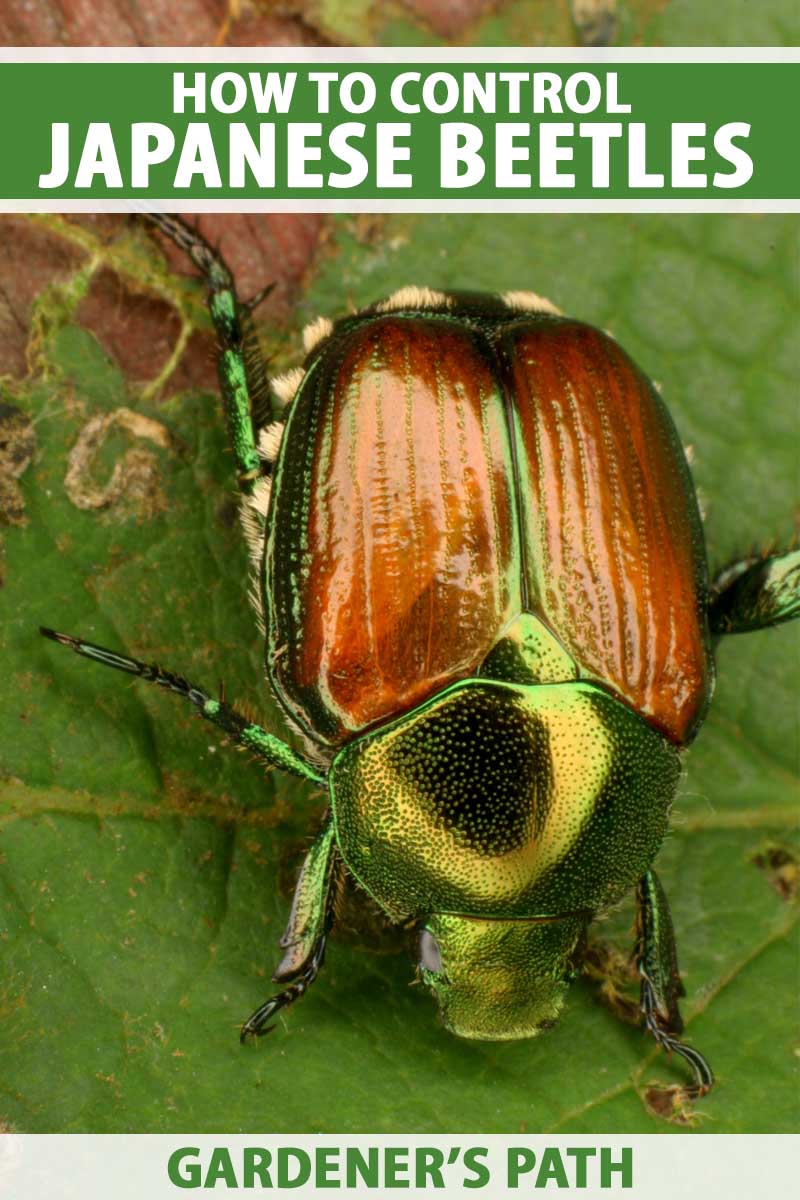
The head and thorax are shiny metallic green and the wing covers are coppery red. The beetle chews away at the leaf tissues to the point where complete defoliation of the deciduous plant material has taken place.
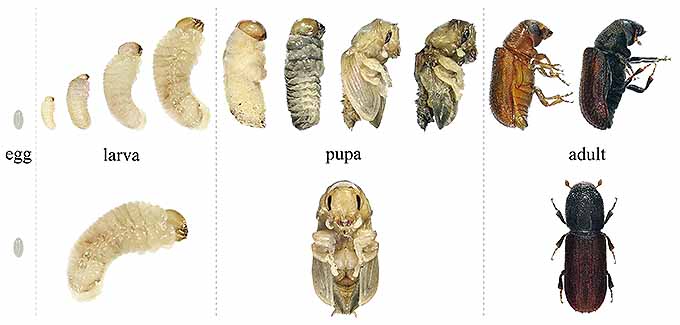
Life Cycle Japanese beetles have one generation per year in Iowa Fig.

. Adult female beetles lay eggs in the soil in early June. They overwinter deep in the soil and resurface again in spring when soil temperatures rise to feed for another 3 to 4 weeks before emerging as adult Japanese beetles. Life cycle of Japanese beetles.
Japanese beetles are similar to other Junebugs in appearance and 38 inch long and 14 inch wide. Adults emerge from grass in late June and immediately begin to feed on low-lying plants such as roses and shrubs. The eggs hatch in about 2 weeks and the developing Japanese beetle larvae white grubs feed on organic matter and grass roots until late fall.
Corn soybean ornamentals fruit trees grapes weeds. The damaging life stage of the Japanese Beetle life cycle is when the white grub is a larvae. Growing degree days accumulated base 50F for Japanese beetle adults in Iowa 1 January-14 June 2015.
The immature stage of the Japanese beetle the white grub typically has a three year life cycle. The eggs hatch into white grubs in ten days to two weeks or longer depend- ing on soil temperature. Japanese beetles were first found in the United States in 1916 near Riverton New Jersey.
Adults eventually move up on trees and field crop foliage to feed and mate. After they emerge the females mate and produce 40-60 eggs. Well established east of the Mississippi River the Japanese beetle is also present in most other corn and soybean growing states.
Applying nematodes in the spring and fall when they live in your soil as grubs can kill the problem before they emerge as adult beetles. Life cycle of Japanese beetles. Life Cycle Japanese beetles have one generation per year in Iowa Photo 1.
Since then Japanese beetles have spread throughout most states east of the Mississippi River. Life Cycle Japanese beetles have one generation per year in Iowa Photo 1. Life Cycle Japanese beetles have one generation per year in Iowa Photo 1.
Adults emerge from grass in late June and immediately begin to feed on low-lying plants such as roses and shrubs. Orkin Termite Treatment Pest Control Exterminator Service. Observing Japanese beetles feeding on plants is quite common since the adult beetle feeds on about 300 species of trees shrubs ornamental and fruit trees in addition to vegetable crops.
Thats because much of its life cycle takes place underground. The appearance of adults the timing of oviposition and subsequent development have been shown to vary with latitude and altitude and also from year to year Fleming 1972. Japanese beetle grubs spend the winter underground in the soil of lawns pastures and other grassy areas.
Japanese beetle grubs are always c-shaped. Japanese beetles that were present last summer laid eggs in moist soil covered with grasses turfgrass waterways. A distinguishing feature of the beetles is five tufts of white hairs on each side of the abdomen.
By Donald Lewis Department of Entomology. Japanese Beetle Life Cycle When Japanese beetles emerge from the ground in late June they burrow 2-3 inches in the ground and begin laying eggs. After the egg hatches in summer the grub feeds on roots until the following summer when it emerges as a shiny beetle.
The larvae feed on roots of grass and other plants close to the surface of the soil. One generation per year. That is it takes one year to complete the development and growth from egg to adult and there is only one generation per year.
However partial infestations also occur west of the Mississippi River in states such as Arkansas Iowa Kansas Minnesota Missouri Nebraska North Dakota Oklahoma and South. Dont worry thats the kind in those. Its not easy to spot the Japanese beetle at first.
The Japanese beetle Popillia japonica has an annual life cycle. Many but not all beautiful insects are good for crops. By late August these grubs are almost full size and will spend the next 10 months in the soil.
The egg larva and pupa life cycle stages develop underground and unless soil is removed or dug into these life stages will not be seen. That is it takes one year to complete the development and growth from egg to adult and there is only one generation per year. Some of the most common trees to suffer dieback from the Japanese Beetle in Des Moines Iowa are the River birch Betula nigra Paper birch Betula papyrifera Linden or American basswood Tilia americana and fruit trees.
Observing Japanese beetles feeding on plants is quite common since the adult beetle feeds on about 300 species of trees shrubs ornamental and fruit trees in addition. Adults begin emergence around 1030 degree days. In most parts of its range the Japanese beetle completes its life-cycle in one year but some populations in cooler climates may complete their development in two years Vittum 1986.
Japanese beetle larvae are annual white grubs. Larvae live in the soil where they feed on plant. This is when grubs are present in the top inch of the root zone heavily feeding on grass roots and thatch.
Only the nematode heterorhabditis bacteriophora is effective in Japanese beetle grub control. Japanese beetles eat more than 300 types of vegetation. Japanese beetles are often found in field edges or areas of delayed growth.
The eggs are laid in the soil and larvae hatch and feed on the roots of plants and grass. Adult beetles start to emerge from the ground in late June or early July. Appearance of adult the timing of oviposition and subsequent development have been shown to vary with latitude altitude and also from year to year Fleming 1972.
The adult beetles lay their eggs in late July into August and the eggs hatch shortly after. Japanese beetle life cycle. Adult females lay eggs in moist sod in July.
The head and thorax are shiny metallic green and the wing covers are coppery red. Each of the first two larval instars stages requires a feeding period of about three weeks. In Iowa adult beetles emerge in mid-June through July.
However most of the damage to ornamentals and turf grass happens during the spring and fall the second year. In spring grubs move up near the soil surface to finish feeding and pupate into adult beetles. Life Cycle In most parts of its range the Japanese beetle completes its life cycle in one year but some populations in cooler climates may complete their development in two years Vittum 1986.
Photo by Erin Hodgson. The grubs are C-shaped and approximately 125 inches when fully grown. While the adult life cycle of the Japanese Beetle is over at the end of the growing season it is always a good time to look ahead.
They can fly up to several miles to feed. Here are the stages in the lifecycle of a Japanese beetle. Consult the life cycle chart for timing or visit the Iowa State University website for some good life cycle information.

Mostly A Good Guy Multicolored Asian Lady Beetle Integrated Crop Management

No Easy Solution For Japanese Beetles Iowa Public Radio
How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles Gardener S Path
Life Cycle Of The Japanese Beetle Including A Eggs David Cappaert Download Scientific Diagram

Information On The Beetle Life Cycle Terminix

Japanese Beetles How To Get Rid Control And Kill Japanese Beetles

How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles In Your Yard

Bioluminescent Bugs Predatory Glow Worms Discovered In Rainforest Webecoist Incredible Creatures Glow Worm Species
White Grubs Phyllophaga And Other Species

Japanese Beetle In Corn And Soybean Integrated Crop Management

Japanese Beetle In Corn And Soybean Integrated Crop Management

Is It Japanese Beetle In The Field Or Something Else Integrated Crop Management

How To Deal With Japanese Beetles Tips That Work

Oddly Insect Outbreaks Reduce Wildfire Severity Insects Reduced Bugs



/June-bug-big-68b1dc172bbf488eabe1d90676a51f01.jpg)
